| Chip Inductor Image Courtesy - www.directindustry.com |
Inductors are also called as storage element because they store energy in their magnetic field. In electric circuits the inductor shown is an idealization of the physical inductor. The practical inductance or inductor or a two terminal element will be called an inductor if at any time t its flux φ(t) and its current i(t) satisfy the relation defined by a curve in the iφ plane. This curve is called the characteristic of the inductor at time t.
An inductor is represented symbolically as shown in figure below,
| Inductor Symbol |
In circuit theory, the fundamental characterization of a two terminal element is in terms of voltage and current. The voltage across the inductor is given by Faraday's Law as ,
v = dφ/dt ..............(1)
where v is in Volts and φ is in Webers (Wb).But we know that
φ(t)= Li(t) ................(2)
where L is constant and is called inductance. The SI unit of Inductor is "Henry" and it is shown by capital letter H.
Therefore equation (1) will become,
v = Ld/dt i(t)...............(3)
Now integrating both sides,
v i(t)/L = d/dti(t)
where i(0) is called inductor current at t=0.
Let us verify this relation between voltage and current that above all equation agrees with Lenz's law; which states that "the electromotive force(emf) induced by a rate of change of flux will have a polarity such that it will oppose the cause of such rate of change of flux."
From equation (1), (2) and (3) we can conclude that
- When the current i(t) increases; that is d/dt i(t) > 0, the flux φ also increases; that is dφ/dt >0.
- Inductors opposes the instantaneous change in current through it.
- Inductors have memory that it shows the property of causality.
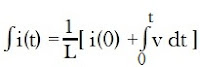



0 comments: