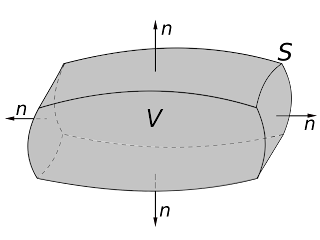
It gives the facility to convert surface integral into its equivalent volume integral.
Statement:- It states that the surface integral of a normal component of any vector function on a closed surface is equal to the volume integral of the divergence of vector function.
Proof:- The total charge enclosed by volume △V is given by
 |
| Representational Image Photo Credit - www.wikipedia.com |
Statement:- It states that the surface integral of a normal component of any vector function on a closed surface is equal to the volume integral of the divergence of vector function.
Proof:- The total charge enclosed by volume △V is given by
........(1)
The total outward flux coming out from the volume is △V equal to the charge enclosed.
△Ψ = △Q = charge density x volume
△Ψ = △Q =ρv△V = ρv△x△y△z.......(2)
From equation (1) and (2)
The divergence of D is given by
From (3) and (4)
According to Gauss's Law
ψ = Q

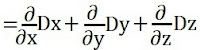

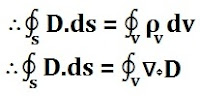



0 comments: